Aplastic Anemia
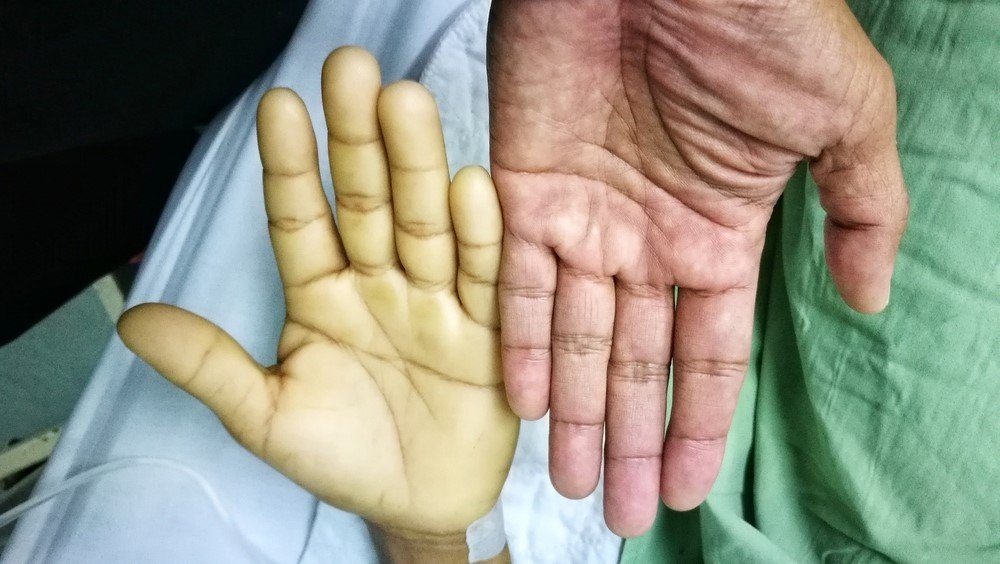
Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious condition where the bone marrow fails to produce sufficient blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This results in a range of complications such as fatigue, increased susceptibility to infections, and bleeding problems. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including autoimmune diseases, exposure to toxins, and certain medications, or it can occur without an identifiable cause.
Causes and Risk Factors of Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia can be caused by various factors, which can be categorized into acquired and inherited conditions. Some of the known causes and risk factors include:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or rheumatoid arthritis can cause the immune system to attack the bone marrow.
- Exposure to Toxins: Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, including benzene and pesticides, can damage the bone marrow.
- Medications: Some drugs, such as certain antibiotics and chemotherapy agents, can cause bone marrow suppression.
- Viral Infections: Viral infections like hepatitis, Epstein-Barr virus, and HIV can lead to aplastic anemia.
- Genetic Factors: Rare genetic disorders such as Fanconi anemia and Dyskeratosis congenita can increase the risk of developing aplastic anemia.
Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
- Fatigue and weakness
- Frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Shortness of breath
- Pale or jaundiced skin
- Dizziness or fainting
Diagnosis
Diagnosing aplastic anemia typically involves blood tests to measure the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. A bone marrow biopsy is also performed to evaluate the number and quality of blood-forming cells in the bone marrow. Additional tests may be conducted to identify any underlying causes or contributing factors.
Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia
Treatment for aplastic anemia focuses on addressing the underlying cause if known and improving bone marrow function. Treatment options may include:
- Blood Transfusions: To manage symptoms and replace deficient blood cells.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: Medications that suppress the immune system to prevent it from attacking the bone marrow.
- Bone Marrow Transplant: Also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, this can potentially cure aplastic anemia by replacing the damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
- Supportive Care: Includes medications to manage symptoms and prevent complications, such as antibiotics for infections and medications to stimulate blood cell production.