Bleeding and clotting disorders
Bleeding and Clotting Disorders
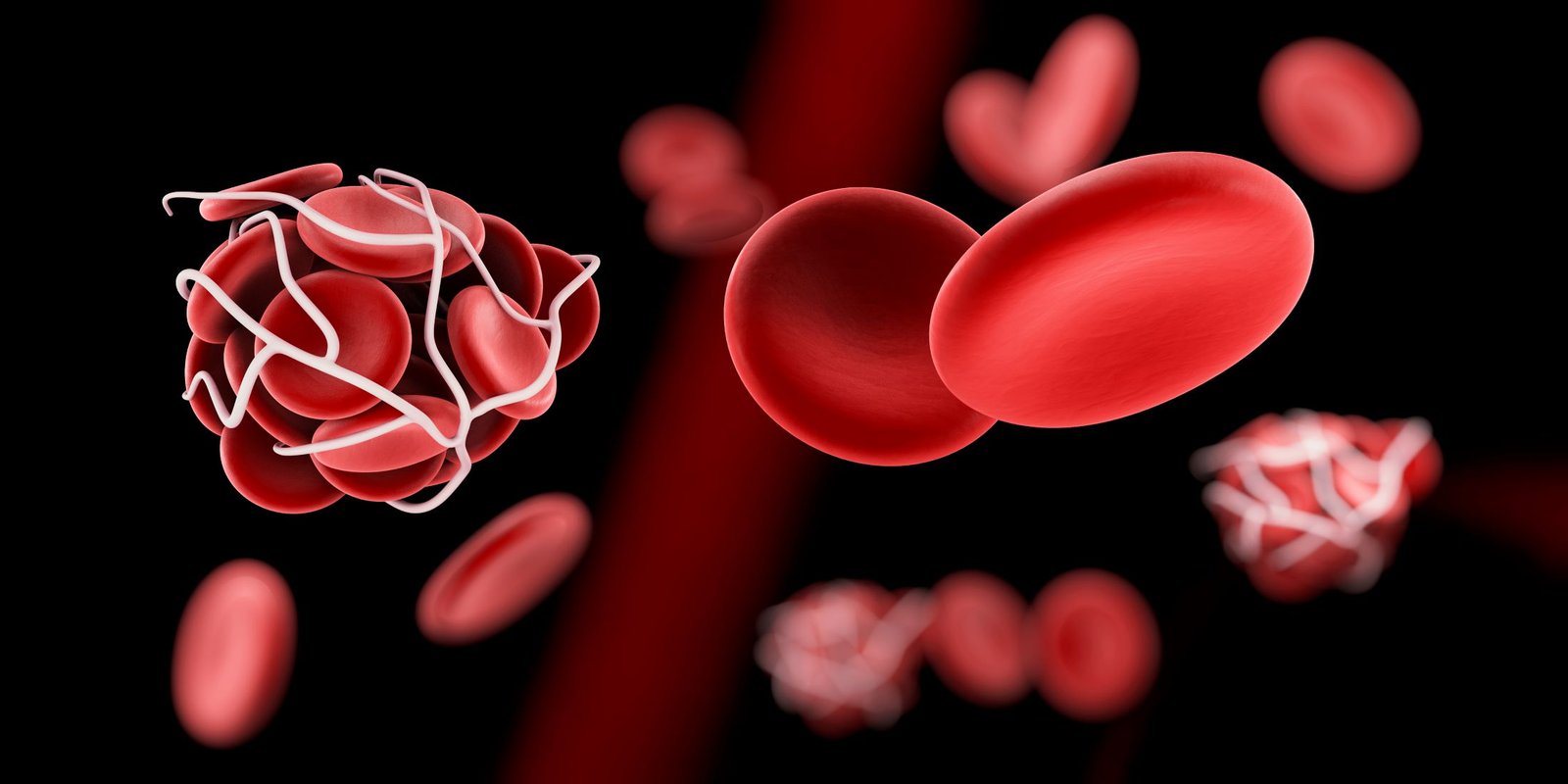
Bleeding and clotting disorders are conditions that affect the blood’s ability to clot properly, leading to either excessive bleeding or abnormal clot formation. These disorders can significantly impact daily life and overall health, and they require careful management to prevent complications.
Types of Bleeding and Clotting Disorders
- Hemophilia : A genetic disorder where blood doesn’t clot properly due to the deficiency of clotting factors. Hemophilia A and B are the most common types.
- Von Willebrand Disease : A bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of von Willebrand factor, a protein crucial for blood clotting.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) : A condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, usually in the legs, which can lead to serious complications if the clot travels to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE) : A blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs caused by a blood clot that has traveled from the legs or other parts of the body.
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome : An autoimmune disorder characterized by the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies that increase the risk of blood clots.
Symptoms of Bleeding and Clotting Disorders
- Excessive or easy bruising
- Frequent or prolonged nosebleeds
- Unexplained or excessive bleeding from cuts or injuries
- Pain, swelling, or redness in the legs (indicative of DVT)
- Shortness of breath or chest pain (indicative of PE)
- Frequent miscarriages (in women with antiphospholipid syndrome)
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing bleeding and clotting disorders often involves blood tests to evaluate clotting factors, platelet counts, and the presence of antibodies. In some cases, imaging studies may be used to identify clots or bleeding sources.
Treatment varies depending on the specific disorder and its severity. Common approaches include:
- Medications: For bleeding disorders, treatments may include clotting factor replacements or desmopressin. For clotting disorders, anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs may be prescribed.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Patients may need to make adjustments to prevent bleeding or clotting, such as avoiding certain medications or activities that increase the risk of bleeding or clots.
- Surgical Interventions: In some cases, procedures may be needed to remove or manage clots, or to address complications associated with bleeding disorders.