Lymphoma
Lymphoma
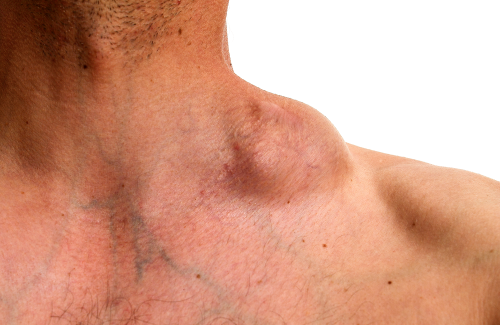
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system. Lymphomas primarily affect lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, causing them to multiply uncontrollably. This leads to the formation of tumors in lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, and other organs.
Types of Lymphoma
- Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL) : A type of lymphoma characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, a specific type of abnormal cell. Hodgkin lymphoma often begins in the lymph nodes of the upper body and is more common in younger adults.
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) : A diverse group of blood cancers that include various subtypes. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma can arise in lymph nodes throughout the body and affects a broader age range, often with varying levels of aggressiveness.
Symptoms of Lymphoma
- Painless swelling of lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin
- Fatigue
- Fever and chills
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats
- Itchy skin
- Shortness of breath or cough
Diagnosis
Diagnosing lymphoma typically involves a physical exam and blood tests, followed by imaging tests like CT or PET scans to look for swollen lymph nodes or tumors. A biopsy of the lymph node is often required to confirm the diagnosis and determine the specific type of lymphoma.