Myelodysplastic syndromes
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
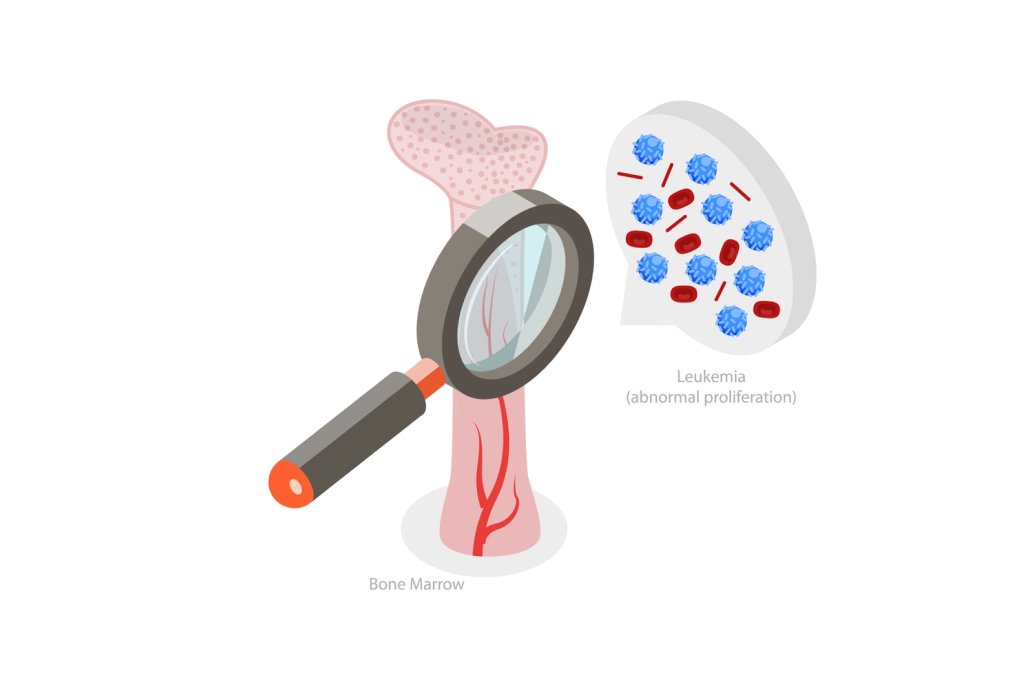
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) are a group of disorders caused by poorly formed or dysfunctional blood cells. These conditions arise when the bone marrow, responsible for producing blood cells, doesn't function properly. MDS can lead to low levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, resulting in symptoms like fatigue, infections, and easy bruising.
Types of Myelodysplastic Syndromes
- Refractory Anemia (RA): Affects red blood cells and leads to anemia, causing fatigue and weakness.
- Refractory Anemia with Ringed Sideroblasts (RARS): Similar to RA, but red blood cells show abnormalities with iron buildup, detected through bone marrow tests.
- Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts (RAEB): This form involves immature blood cells (blasts), which can develop into acute myeloid leukemia if left untreated.
- Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML): Shares characteristics of both MDS and leukemia, affecting the bone marrow and blood.
Symptoms of Myelodysplastic Syndromes
- Fatigue and weakness
- Frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Shortness of breath
- Paleness or pale skin
- Unexplained weight loss
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Myelodysplastic Syndromes involves blood tests to assess levels of blood cells, often a complete blood count (CBC). A bone marrow biopsy is typically conducted to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the extent of abnormal cell production.